The spine consists of bones (vertebrae) and rubbery disks that form the spinal canal. The discs are small and round, with tough outer layers that shield the vertebrae. They are situated between each vertebra, act as buffers for the spinal bones, and allow us to bend and move without difficulty. A herniated disk is a result of damage to the rubbery disks. The injury commonly causes pain in the neck, leg, and back. A herniated disc is an all too common yet crippling medical condition. Here is a breakdown of the common causes, treatments, and prevention.
What is a Herniated Disc?
Herniated discs, otherwise known as slipped or ruptured discs, are a medical condition that may happen in the neck or the lower back. It occurs when a segment of the disc’s nucleus is displaced/pushed out into the spinal canal through a ruptured or torn outer layer(annulus). This results in the disc pressing on spinal nerves and thus generating pain.
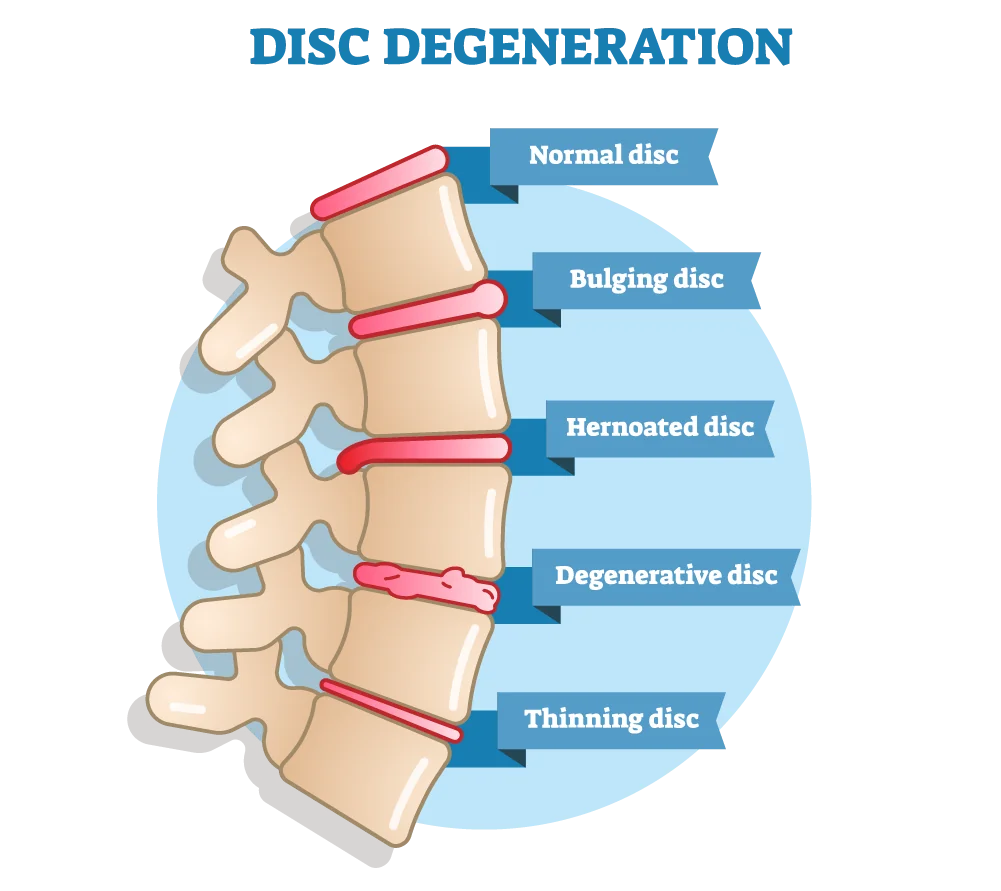
Differences Between Herniated and Bulging Discs
While both affect the vertebral discs, a bulging and herniated disc are two individual terms of different conditions.
- A bulging disc drives the disc’s inner core (nucleus pulposus) on the spinal canal, while in a herniated disc, the nucleus pulposus escapes into the outer layer entirely.
- A herniated disc characteristically shows instantly in acute pain, whereas a bulging disc may be undetected for some time until symptoms worsen.
- The bulging disc is the primary type of disk injury, while the herniated disc is not common.
- Bulging discs bring about pain in the limbs, back, head, and nearby areas, while herniated discs bring intense pain in the same areas.
- Herniated discs are characterized by a tear or rupture in a disc’s outer layer, whereas bulging discs are characterized by swelling and bulging of the disc’s inner core.
Clinical Manifestations
The signs and symptoms of a herniated disc vary based on the location of the disc and the affected nerve root. The most common clinical manifestations include:
- Unexplained muscle weakness in lower limbs
- Changes in bowel and bladder function
- Diminished reflexes at the ankle or knee
- Burning, aching, or tingling sensations in the affected area; arms, feet, back, legs, or hands.
- Sciatica- pain that spreads to the lower limb
- Back muscle spasms
- Recurrent back pain that may worsen by sneezing, coughing, or movement

These symptoms can be excruciating for most individuals and may clear up themselves. Generally, it is thought that the symptoms are alleviated because the decreased size of the herniation lessens the probability of irritation of the nerve root. Experts believe that the symptoms resolve themselves for the following reasons:
- Lumbar extension exercises that may move the herniated out of the spinal discs
- The herniation is attacked as a foreign substance by the body, shrinking its size and bringing down the inflammatory proteins in the nerve root.
- With time, some of the water from the disc is assimilated into the body, thus resulting in a shrunk disc.
Herniated Disc Causes and Prevention
Herniated discs are brought about by the change in the structure of a disc, often due to age-related wear and tear of the spine, otherwise known as disc degeneration. However, certain factors can develop risks of the condition occurring.
Risk Factors
The factors that build up the risk of disc herniation include:
- Overweight
- Gender: Men are twice as likely to get a herniated disc between 30 and 50 years of age than women
- Repetitive activities that strain the spine, such as those that need constant lifting, pulling, or bending
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Driving for long periods
- Improperly lifting heavy objects.
Prevention
The following ways can help prevent disc herniation:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Improving posture when walking, standing, or sitting.
- Regularly exercising
- Employing proper lifting methods
- Avoiding the use of any tobacco

Testing and Diagnosis
Your doctor will conduct a thorough examination evaluating your muscle strength, reflexes, and pain and may also order one of the following tests:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- X-ray
- Myelogram
- CAT scan
- Electromyography (EMG)
Treatment
Approximately 85% of individuals with a herniated disc recover without needing treatment. However, the first line of treatment for those with severe symptoms is usually non-surgical, which helps manage the condition.

Non-surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatments that help relieve your symptoms may include:
- Bed rest is usually recommended for two or three days to alleviate intense back and leg pain.
- Physical therapy may be recommended to vitalize your abdominal muscles and lower back.
- Epidural steroid injections may deliver temporary pain relief by bringing down the inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants may be prescribed.
- Applying ice or heat to the affected area may also help alleviate pain.
Surgery
If the non-surgical treatments fail to be effective, your doctor may recommend surgery. Surgical techniques for herniated discs include the following:
- Discectomy: Entails removal of all or a section of the affected disc
- Laminectomy: The surgeon may get rid of a section of vertebrae to make room for nerves
- Disc replacement: Herniated discs are substituted with artificial implants
- Spinal fusion: The procedure entails connecting two or more vertebrae
- Nucleotomy: Entails the removal of the nucleus of the disc via laser excision or suction
At ProActive Physical Therapy, we take pride in our patient’s results. We offer hands-on therapy with a customized plan tailored to help you heal and get your healthy life back. If you are experiencing any symptoms related to herniated discs or would like a free consultation to understand the causes and prevention, schedule today for an appointment.